What are the future scenarios for Germany regarding their climate and situation??
Air Temperature increase:
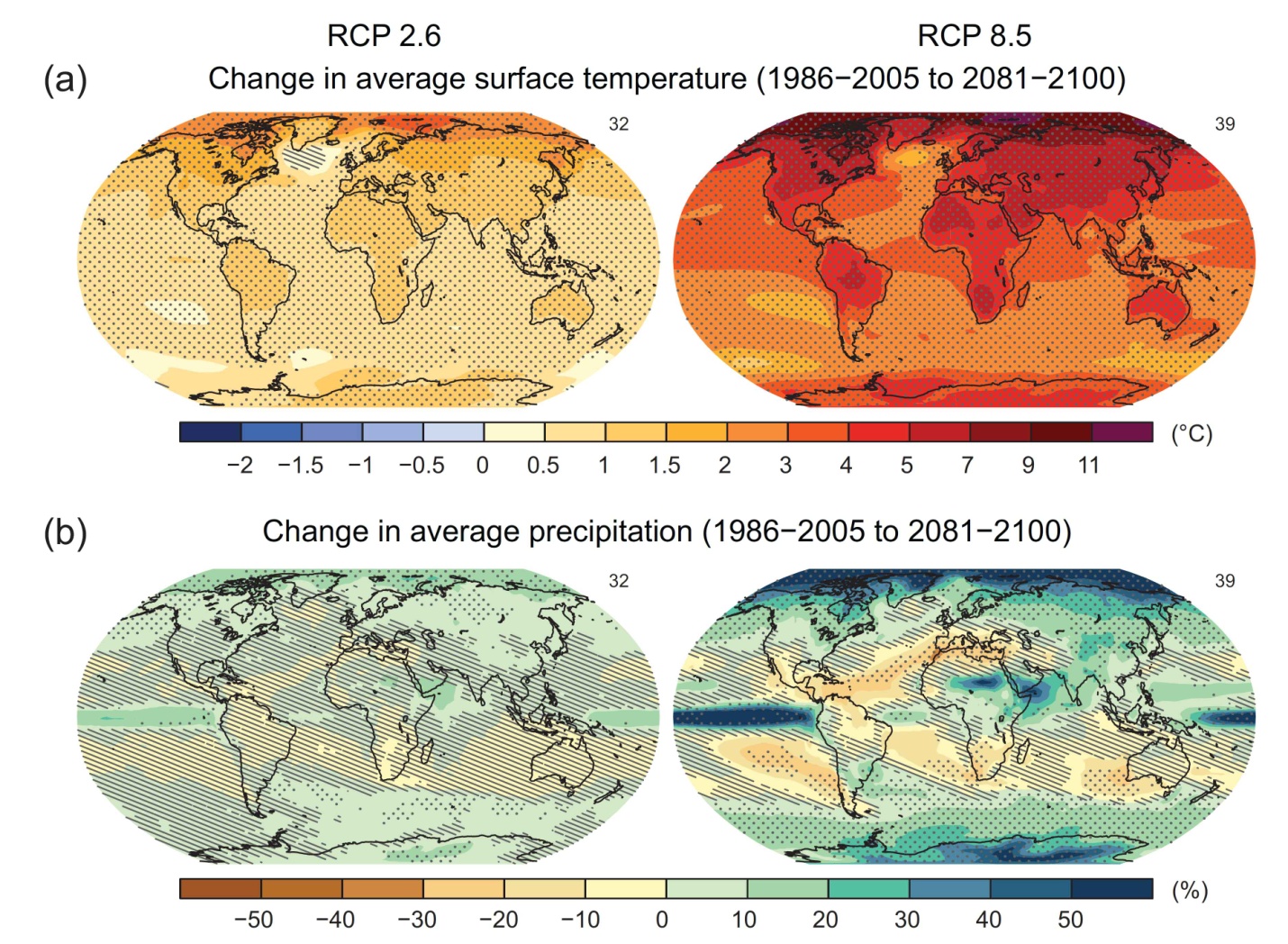
Temperatures are expected to increase by 0.5-1.5 degrees Celsius within the year period 2021-2050. This is based off of the past data from 1961-1990.
According to several other climate scenarios the long-term annual temperature in Germany is projected to rise by 1.6-3.8 degrees Celsius by the year 2080.
The southwest and some of the eastern regions have many scenarios pointing to strong warming conditions.
According to climatechangepost.com, some scenarios suggest that the number of summer days could double by the end of the century, and the number of hot days could even be projected to triple.
Precipitation scenarios for the future:
Several lower mountain ranges and river valleys in Southern Germany are subject to changes in mean and extreme precipitation where in the winter the study area became moister (5-10%).
In the summer there are slight decreases of precipitation in Central Europe for the near future.
In regards to the long term (end of the 21st century) the several climate scenarios show very little changes that mostly lie below 10% until 2080.
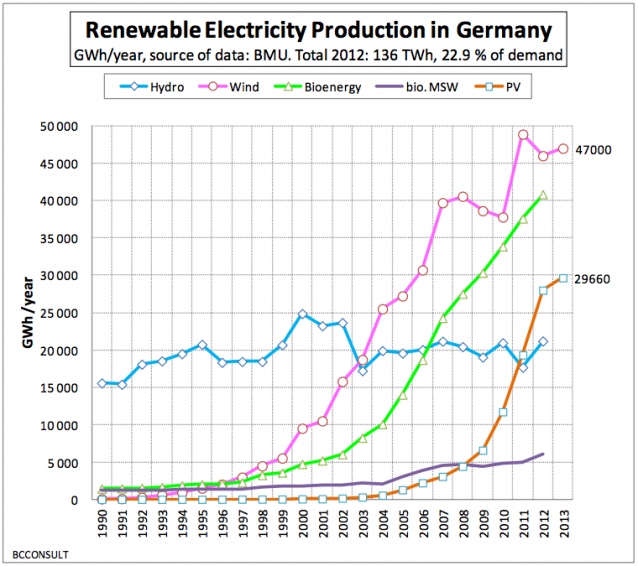
Germany has been trying to lead the retreat from fossil fuels since the early 1990's. Germany is pushing away from the nuclear power plants and aiming towards more of a renewable energy society, in which they actually are able to resell all their excess energy/utilities to the government.
Germany actually plans to shut all its reactors by the year 2022 in an effort to revert the energy consumption from fossil fuels and nuclear power to wind, solar, and hydro powered.
 |
| http://ngm.nationalgeographic.com/2015/11/climate-change/germany-renewable-energy-revolution-text This picture shows a newly built, never been used, nuclear reactor in Kalkar, Germany. |
Another aspect of the economy that Germany is trying to alter in an effort to halt climate change is within their car industry. Companies like Volkswagen, Daimler, Porsche, and BMW all have or will soon launch their own versions of electric cars. And some of the car companies have announced an end to the diesel rush.
 |
| http://inhabitat.com/all-new-cars-in-germany-must-be-emissions-free-after-2030/ This image shows Germany's efforts to push electric vehicles popularity |
 |
| http://knowledge.wharton.upenn.edu/article/can-the-world-run-on-renewable-energy/ A cleaner world for a cleaner life! |
This rule has been part of Germany's broader goal to slash their carbon dioxide emissions up to 95% by 2050.
With Germany leading the push for alternatives to fossil fuel energy, they are constantly breaking grounds for new energy efficient technologies. They stand as a leader among the world powers in climate change efforts and prevention. Germany, a country which had to rebuild itself after WWII, also acts as a role model for up and coming nations who are not exactly in line with the world powers when discussing the climate change efforts and possibilities.
.svg/1280px-Flag_of_Germany_(unoff).svg.png) |
| German Flag and Coat of Arms |
Works Cited
- http://ngm.nationalgeographic.com/2015/11/climate-change/germany-renewable-energy-revolution-text
- http://www.climatechangepost.com/germany/climate-change/
- https://www.carbonbrief.org/timeline-past-present-future-germany-energiewende